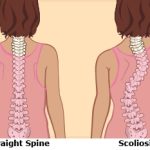
Can Scoliosis Cause Chest Pain? Understanding Causes and Treatment
Yes, scoliosis can cause chest pain, especially when the spinal curve affects the thoracic spine, which is connected to the rib cage. The abnormal sideways curvature of the spine seen in scoliosis can put pressure on the ribs, muscles, and organs like the lungs and heart. This can lead to discomfort and chest pain. Below, we explain how scoliosis causes chest pain, which types of scoliosis are linked to this symptom, and how it affects other parts of the body.
How Scoliosis Leads to Chest Pain
1. Rib Cage Deformity and Compression
In thoracic scoliosis, the spine not only curves but may also twist, causing the ribs to become uneven. One side of the rib cage may protrude more, causing what’s known as a “rib hump.” This imbalance can compress organs in the chest cavity, including the lungs and heart, which may result in chest pain, especially when taking deep breaths or during physical activity. Additionally, rib deformation may irritate the intercostal nerves, leading to sharp or dull chest pain.
2. Lung Function Problems
Severe scoliosis can reduce lung capacity by restricting the expansion of the rib cage, leading to a condition called restrictive lung disease. This can cause:
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing deeply due to reduced lung capacity, especially during physical exertion, can cause chest discomfort.
- Muscle Strain: The diaphragm and rib muscles have to work harder when lung function is reduced, leading to muscle strain and pain in the chest.
Scoliosis curves greater than 70 degrees are more likely to cause significant breathing difficulties and chest discomfort, though less severe cases can also have minor effects.
3. Heart Function Impact
In rare and severe cases, scoliosis can affect heart function. When the curvature compresses the rib cage, it can impact the heart and blood vessels, leading to:
- Poor Circulation: The pressure on blood vessels may restrict circulation, causing chest tightness or discomfort.
- Heart-Lung Complications: A combination of lung and heart function issues may result in chest pain, especially during activities that increase oxygen demand.
4. Muscle and Joint Strain
Scoliosis causes muscle imbalances around the spine, which can result in:
- Muscle Spasms: Uneven muscle strain can cause spasms in the back and chest muscles, leading to chest pain.
- Postural Imbalance: The spine’s abnormal curve often causes poor posture, putting additional strain on the chest and back muscles, leading to discomfort.
The uneven rib alignment also stresses the costovertebral joints (where the ribs meet the spine), leading to inflammation and pain in the chest and upper back.
5. Referred Pain
Scoliosis can cause referred pain, where the pain originates in one area (such as the spine) but is felt in another, such as the chest. This type of pain can manifest as sharp, burning, or aching sensations in the chest area.
Types of Scoliosis Linked to Chest Pain
- Thoracic Scoliosis: Curvature in the thoracic (mid-back) region is the most common cause of scoliosis-related chest pain due to its proximity to the ribs and lungs.
- Severe Scoliosis: Chest pain is more common in cases where the spinal curvature exceeds 50 degrees, putting greater pressure on the rib cage, lungs, and heart.
- Kyphoscoliosis: A combination of scoliosis (sideways curve) and kyphosis (forward curve) can result in severe chest deformities, increasing the likelihood of chest pain.
Managing Chest Pain from Scoliosis
If scoliosis causes chest pain, these methods can help:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises that improve posture and strengthen spinal muscles can relieve tension and reduce chest pain.
- Breathing Exercises: Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing can help improve lung capacity, reducing chest discomfort.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications can ease muscle strain and inflammation in the chest.
- Bracing: For moderate scoliosis, wearing a back brace can help prevent the spinal curve from worsening and reduce chest pressure.
- Surgery: In severe cases, spinal surgery may be required to correct the curvature and alleviate pressure on the lungs, heart, and rib cage.
Conclusion
Scoliosis can cause chest pain, especially when the spine’s curve affects the thoracic region. Rib cage deformities, lung compression, and muscle strain are all potential causes of chest discomfort. Severe cases of scoliosis, particularly those with curves over 50 degrees, are more likely to experience chest pain due to the impact on the lungs and heart. Managing scoliosis-related chest pain involves physical therapy, breathing exercises, pain management, and, in extreme cases, surgery to correct the spine.
By addressing the root causes of chest pain, scoliosis patients can improve their quality of life and reduce discomfort.